By doing so, we can analyze the proportions and relationships between different components of the income statement. While horizontal analysis remains valuable for assessing changes over time, vertical analysis offers unique perspectives and granularity in financial analysis. Accurate and reliable financial statements are essential for conducting effective vertical analysis. If the financial statements contain errors or are not prepared in accordance with accounting principles, the results of vertical analysis may be misleading.
- Fourth, horizontal analysis can be calculated in absolute terms or percentage terms as desired.
- Previously, Stefan served as the Corporate Controller for Kodiak Cakes, a private equity owned, leading consumer packaged food company, and as a Controller for Skullcandy, a multinational headphone CPG.
- Vertical analysis revolves around the idea of converting financial statement items into percentages of a base figure, which simplifies the comparison of financial data.
- This simplicity and clarity enables efficient evaluation of a company’s financial health and performance, leading to more effective strategic decision-making by executives.
- Vertical analysis is a kind of financial statement analysis wherein each item in the financial statement is shown in the percentage of the base figure.
- An analyst may first look at a number of ratios on a company’s income statement to determine how efficiently it generates profits and shareholder value.
- We can gather from the data below that the sales of the company increased consistently from year 1 to year 3.
Understanding the Impact of Vertical Analysis on Profitability Evaluation
Converting static figures into percentages in terms of the baseline item helps create a trend series. Analysts can then use it for internal performance evaluation across multiple accounting periods. Vertical analysis is a common tool to analyze financial statements comparatively in a single accounting period. Second, vertical https://www.bookstime.com/ analysis compares items on a financial statement in relation to each other.

Evaluate balance sheet composition

By the end of this guide, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge to interpret vertical analysis results and apply them in practical scenarios. The following example shows ABC Company’s income statement over a three-year period. The vertical analysis provides several advantages to internal and external stakeholders of a company. Therefore, if you want to compare the performance of a company across accounting periods, you’ll have to conduct separate vertical analyses for each accounting period. Input the percentage against the line items calculated to see a concise view of each item’s contribution to the gross amount.

Vertical Analysis Vs Horizontal Analysis – Key Differences
Usually, the purpose of horizontal analysis is to detect growth trends across different time periods. For instance, we can observe that the cost of goods sold represents 40% of net sales, indicating that the production or procurement of goods consumes 40% of the revenue. The gross profit margin is 60%, suggesting that the company retains 60% of its revenue after deducting the cost of goods sold. We can discern through vertical analysis that the main problem area vis-à-vis the decline in net income in year 3 is the cost of goods sold.
External stakeholders use it to understand the overall health of an organization and to evaluate financial performance and business value. Vertical analysis of financial statements is also very useful in analyzing key trends over time. For example, through vertical analysis, we can assess the changes in petty cash the working capital or fixed assets (items in balance sheet) over time. Cash in the current year is $110,000 and total assets equal $250,000, giving a common-size percentage of 44%.
- Most often, analysts will use three main techniques for analyzing a company’s financial statements.
- By expressing line items as percentages of a base figure, you can identify trends, assess proportions, and gain valuable insights into a company’s financial performance.
- Vertical analysis expresses each item on a financial statement as a percentage of the total.
- Or, it might indicate an excess in company headcount, necessitating a thorough review.
- This helps in evaluating the efficiency of cost management which thus identifies areas of improvement.

Most often, analysts will use three main techniques for analyzing a company’s financial statements. You can compare companies in the same industry by standard comparisons of key line items. By comparing other companies’ percentages against your own, you can understand the strengths, weaknesses, and changes you will need to make. Vertical analysis lets you identify trends, growth areas, and patterns in your financial statements and build well-informed strategic plans. Vertical analysis is a method of financial analysis where each line item is listed as a percentage of a base figure within the statement.
Key Learning Points
- Understanding the relationship between different line items within the financial statements can provide FP&A professionals to make assumptions about the future composition and allocate resources accordingly.
- It helps identify the impact of changes in asset or liability categories on the overall financial health of the organization.
- Let’s look at an example to see how applying the vertical analysis formula might work in the real world.
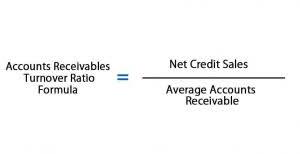
- It could possibly be that they are extending credit to customers more readily than anticipated or not collecting as rapidly on outstanding accounts receivable.
- We discussed how to interpret the results, considered limitations, and highlighted practical applications.
- Horizontal analysis can then be used to track how these marketing expenses have changed over the past five years.
Vertical analysis (also known as common-size analysis) vertical analysis formula is a financial statement analysis technique that shows each line item on a financial statement as a percentage. Let’s look at vertical analysis in more detail, explore how it works and examine the differences between vertical analysis and horizontal analysis. In this example, we have expressed each line item as a percentage of the total assets, which serves as the base figure. This allows us to assess the proportions and relationships between different components of the balance sheet. In addition, vertical analysis can aid in financial forecasting by projecting future trends based on historical data.




